How Google Finds, Processes, and Ranks Your Website
Google crawling, indexing, and ranking are the three fundamental stages that determine if and where your website appears in search results. Understanding this fully automated process is the first step to improving your site’s visibility.
The Three Stages of Google Search:
- Crawling: Google’s bots (Googlebot) find your web pages by following links and reading sitemaps.
- Indexing: Google analyzes your page content and stores it in a massive database called the Google Index.
- Ranking: When a user searches, Google’s algorithms sort through indexed pages to show the most relevant, high-quality results.
In short, crawling is finding your pages, indexing is understanding them, and ranking is ordering them. Google doesn’t accept payment to crawl a site more frequently or rank it higher.
This process is critical for franchise businesses. Without proper crawling, your location pages won’t be found. Without indexing, they won’t be stored. And without optimization, they won’t appear when customers search for your services.
As Rusty Rich, President of Latitude Park, I’ve spent over 15 years helping businesses master google crawling, indexing, and ranking. This guide will break down each stage and show you how to optimize your website for maximum visibility.
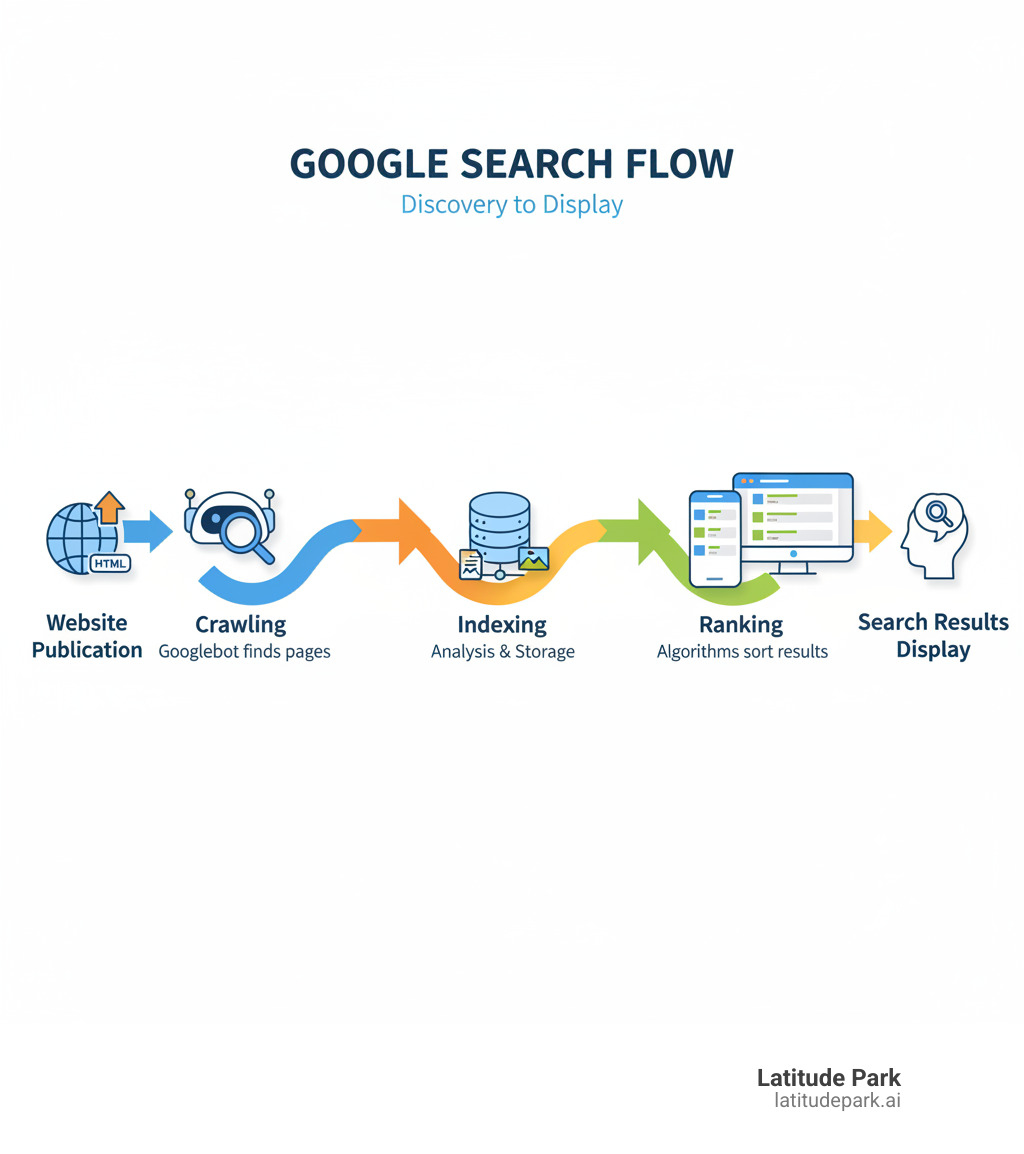
What’s the Difference Between Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking?
These three stages are distinct but sequential. Each serves a unique purpose in getting your content seen by potential customers.
| Aspect | Crawling | Indexing | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Finding new and updated web content. | Understanding and Storing content in Google’s database. | Ordering the most relevant results for a user’s query. |
| Process | Googlebot follows links and reads sitemaps to find pages. | Google analyzes text, images, and metadata to categorize information. | Algorithms evaluate hundreds of factors to determine the best match for a search. |
| SEO Control | Sitemaps, robots.txt, internal linking, server health. | Meta robots tags (noindex), canonical tags, content quality. | Content quality, backlinks, site speed, mobile-friendliness, user experience. |
Crawling is the initial findy phase, indexing is the organization phase, and ranking is the final ordering phase. A strong foundation in all three is essential for SEO success, a vital part of digital media marketing as explained in our guide on The importance of SEO in digital media marketing.
Stage 1: Crawling – How Google Finds Your Content
Crawling is the first step in getting your website noticed by Google. If Google’s crawlers, known as Googlebot or “spiders,” don’t visit your pages, they effectively don’t exist in Google Search.
Googlebot finds new pages primarily by following links from other websites and within your own site. It also uses sitemaps you submit via Google Search Console to find your most important pages. Finally, it revisits previously crawled pages to check for updates.
A crucial part of this process is rendering. Googlebot renders your page using a recent version of Chrome, executing JavaScript just as a user’s browser would. If Google can’t render your JavaScript correctly, it may miss critical content, harming your site’s ability to be indexed and ranked.
For franchises, each location page must be findable through clear internal links and sitemap submissions. Learn more about getting found online in How to put your business on Google: A step-by-step guide.
Factors Influencing Google’s Crawl
Google’s crawl frequency and speed depend on several factors:
- Crawl Budget & Rate: This is Google’s estimate of how many URLs it can and should crawl on your site without causing performance issues. A fast, healthy site encourages more frequent crawling.
- Crawl Demand: High-quality content, regular updates, and strong backlinks signal to Google that your site is worth visiting often.
- Site Health & Server Speed: A fast server with minimal errors (like 5xx server errors) allows Googlebot to work efficiently. Slow load times or frequent outages will reduce crawling. Optimizing server performance, as discussed in Leverage browser caching: Speed website, can significantly improve crawl efficiency.
- Page Freshness & Importance: Regularly updated content on key pages, identified through strong internal linking, signals that your site is active and valuable.
How to Guide Googlebot with Sitemaps and Robots.txt
You can provide clear instructions to Googlebot using two key files:
- XML Sitemap: This file acts as a directory of all the pages you want Google to crawl. Submitting a sitemap via Google Search Console is a powerful way to guide Google, especially for new or large sites. For more, see Google’s sitemaps documentation.
- Robots.txt: This file tells crawlers which parts of your site to avoid. Use disallow directives to block access to admin pages, staging environments, or other non-public areas. A misconfigured robots.txt can accidentally block important content, so handle it with care. Refer to Google’s guide on how to Create and Submit a robots.txt File.
Common Crawling Issues and How to Fix Them
Regularly check Search Console to identify and fix these common issues:
- Server Errors (5xx): Indicate a problem with your server. Work with your hosting provider to resolve them.
- Not Found Errors (404): Occur when a page no longer exists. Use 301 redirects for moved content and ensure no internal links point to deleted pages.
- Blocked by robots.txt: Your robots.txt file is accidentally preventing Google from crawling important pages. Use Google’s Robots.txt Tester to audit your file.
- Infinite Spaces: Dynamic URLs (e.g., from calendars or filters) can trap Googlebot. Block these URL patterns with robots.txt or use canonical tags.
- Redirect Chains: Multiple redirects slow down crawling and dilute ranking signals. Consolidate them into a single 301 redirect to the final destination.
Fixing crawling issues is as important as monitoring your rankings, a topic we cover in How to check the ranking of my website.
Stage 2: Indexing – How Google Understands and Stores Your Pages
After crawling, Google analyzes, categorizes, and stores your content in its massive database, the Google Index. This is the indexing stage, where Google acts like a librarian for the web.
During indexing, Google reads your content to understand its topics, keywords, and context. It also analyzes metadata like your title tags and meta descriptions. Your title tag becomes the clickable headline in search results, and the meta description serves as the summary beneath it.
Google also notes a page’s language, geographic relevance, and usability signals. Critically, Google now uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily evaluates the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking. If your mobile site offers a poor experience or is missing content, your search performance will suffer.
Proper indexing is fundamental to all google crawling, indexing, and ranking strategies. Without it, your content is invisible. For more on this, see The ultimate guide to on-page SEO.
What Makes a Page Eligible for Indexing?
Google doesn’t index every page it crawls. To be indexed, a page must meet certain criteria:
- High-Quality and Helpful Content: Your page must offer genuine value by answering questions, solving problems, or providing unique insights. Thin or unhelpful content is often ignored. Refer to Google’s helpful content guide for more.
- Originality: Google prioritizes unique content. If your page is a copy of what’s already available, it’s unlikely to be indexed.
- No ‘noindex’ Tag: A
meta name="robots" content="noindex"tag in your page’s HTML explicitly tells Google not to index the page. - Accessibility: The page must not be password-protected or blocked by server errors, as Googlebot cannot index what it cannot access.
For franchises, maintaining content quality across all locations is key. Our guide on Creating SEO-friendly content: Tips & Best Practices offers practical strategies.
Handling Duplicate Content and Canonicalization
Duplicate content occurs when multiple URLs show the same or very similar content. This is common on e-commerce sites with product variants or franchise sites with similar location pages. When Google finds duplicate content, it groups the pages into a cluster and selects one canonical URL to show in search results.
This process, called canonicalization, consolidates ranking signals (like backlinks) to a single, authoritative page. You can guide Google by using the canonical tag (rel="canonical"). This tag, placed in the HTML header of a duplicate page, points to your preferred version.
For example, if example.com/product?color=red is a variation of example.com/product, you would add a canonical tag on the red version pointing to the main product page. This tells Google which page to prioritize for indexing and ranking.
Understanding How Google handles duplicate content is crucial for multi-location brands. Our guide on On-page SEO tactics: Multi-location brands dives deeper into solving these specific challenges.
Stage 3: Ranking – How Google Orders Search Results
Ranking is the final stage, where Google decides which pages to show for a search query and in what order. This is where google crawling, indexing, and ranking culminates, determining whether customers find you.
When someone searches, Google’s ranking algorithms evaluate billions of indexed pages against hundreds of signals to deliver the most helpful answer. These algorithms aim to understand search intent—what the user truly wants. A search for “pizza” on a phone likely means the user wants to order from a nearby restaurant, while “how to make pizza dough” implies they want a recipe.
To rank well, your content must have relevance to the query, come from an authoritative source, and provide a good user experience. Search results are also personalized based on location, device, and search history, which is beneficial for franchises aiming to attract local customers.
To learn more, explore How to rank higher on Google: 10 effective strategies.
Key Signals Google Uses for Ranking Pages
While the exact formula is secret, we know many key ranking signals:
- Content Relevance and Quality: The page must comprehensively and accurately answer the user’s query.
- Backlinks: Links from reputable, relevant websites act as votes of confidence, signaling authority to Google. Quality matters more than quantity. Learn more in Why dofollow backlinks are crucial for ranking.
- Page Speed: Faster-loading sites are rewarded. Core Web Vitals measure loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability.
- Mobile-Friendliness: With mobile-first indexing, your site must function perfectly on mobile devices.
- E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness are crucial, especially for topics affecting a person’s health or finances.
- User Context: Factors like location, language, and device type influence results, making local SEO vital for franchises.
- Website Security: HTTPS is a standard requirement and a minor ranking signal.
The Role of AI and System Updates in Ranking
Google Search is constantly evolving, driven by AI and regular system updates.
- AI in Search: Technologies like BERT and MUM help Google understand the nuances of language and user intent, leading to more accurate results. As Google’s article on Nine ways that we use AI explains, AI is deeply integrated into its products.
- Helpful Content System: This site-wide signal rewards content created for people, not just for search engines. It demotes sites with unhelpful, low-quality content.
- Core Updates: These broad changes to ranking systems, released several times a year, can cause significant shifts in search results. The best defense is a long-term, user-focused SEO strategy.
- Spam Detection: AI-powered systems automatically identify and filter out spam and manipulative tactics.
The rise of AI means creating genuinely valuable content is more important than ever, a shift we explore in Importance of SEO in the age of AI.
How to Master Google Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking
Mastering google crawling, indexing, and ranking requires seeing them as a unified whole. If Google can’t crawl your pages, they won’t be indexed. If they aren’t indexed, they can’t rank. It’s all connected.
A comprehensive SEO strategy is built on three pillars:
- Technical SEO: Ensures your site’s infrastructure is solid, allowing crawlers to access and index content without issues. This includes site speed, mobile-friendliness, and a clean URL structure.
- On-page SEO: Optimizes individual pages with relevant keywords, compelling title tags, and structured content to make them understandable to search engines.
- Off-page SEO: Builds your site’s authority, primarily by earning high-quality backlinks from reputable websites.
These pillars are held up by a strong content strategy. Helpful, engaging content is what attracts visitors, earns links, and drives business. For franchises, coordinating this across multiple locations is a complex but critical challenge.
For more on this, see Effective SEO techniques to improve your website’s search ranking and 8 reasons why every business should have an SEO strategy.
Best Practices for Google Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking
Here are battle-tested strategies that consistently deliver results:
- Optimize Site Structure: Create a logical hierarchy so important pages are easily accessible. Use descriptive anchor text for internal links to distribute ranking power.
- Create High-Quality Content: This is the most important factor. Write for people, not search engines, by providing original, comprehensive content that solves user problems.
- Ensure Fast, Mobile-Friendly Design: Your site must work flawlessly on all devices. Optimize images, streamline code, and monitor your Core Web Vitals.
- Manage Robots.txt Carefully: Use it to block non-essential sections, but regularly audit the file to ensure you aren’t blocking important content.
- Submit Accurate XML Sitemaps: Keep your sitemap updated and submitted via Google Search Console to give Google a clear roadmap to your content.
- Use Canonical Tags Correctly: For duplicate or similar content, use
rel="canonical"tags to consolidate ranking signals to your preferred URL. - Build Quality Backlinks: Focus on earning links from authoritative, relevant websites in your industry.
- Optimize On-Page Elements: Craft compelling title tags and meta descriptions. Use header tags (H1, H2) to structure content logically.
- Fix Technical Errors Promptly: Regularly monitor and fix 404 errors, server issues, and redirect chains to avoid wasting crawl budget.
Tools to Monitor and Improve Your SEO Performance
Several powerful tools provide the insights needed to track your progress:
- Google Search Console: This free tool is essential. It provides data on crawl errors, indexing status, search queries, and mobile usability. The URL Inspection Tool is invaluable for troubleshooting specific pages.
- PageSpeed Insights: Analyzes your page’s loading performance and provides actionable recommendations to improve Core Web Vitals.
- Mobile-Friendly Test: A quick check to verify your pages work correctly on mobile devices. Find it at https://search.google.com/test/mobile-friendly.
- Robots.txt Tester: Found in Search Console, this tool helps you verify your robots.txt file works as intended before you deploy changes.
Understanding your competition is also key. Our guide on Competitor Keyword Research: Is it really that important? can help sharpen your strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my page crawled but not indexed?
This common issue occurs because crawling doesn’t guarantee indexing. Google may crawl a page but decide not to add it to its index for several reasons:
- Low-Quality Content: The page may be considered thin, unoriginal, or unhelpful to users. Google is selective and avoids indexing low-value content.
- ‘Noindex’ Directive: The page might have a
meta robotstag or anX-Robots-TagHTTP header explicitly telling Google not to index it. Double-check your page’s code and server configuration. - Canonicalization Issues: Google may have identified your page as a duplicate of another and selected the other page as the canonical version to index. We explain this in our section on How Google handles duplicate content.
- Manual Action: In rare cases, your site may have a manual penalty for violating Google’s guidelines. Check the Manual Actions report in Google Search Console.
- Technical Rendering Issues: If your site relies on JavaScript, Google may have failed to render the page correctly, preventing it from seeing the full content.
How long does it take for Google to crawl and index a new page?
The time it takes can range from a few days to several weeks. It depends on several factors:
- Site Authority: Well-established, trusted sites that publish frequently are crawled more often, and new content is typically indexed within days.
- Crawl Rate: A healthy site with a fast server encourages Googlebot to visit more frequently.
- Sitemap Submission: Submitting an updated XML sitemap through Google Search Console notifies Google about new content.
- Internal Linking: Linking to your new page from existing, well-indexed pages helps Googlebot find it faster.
For important pages, you can use the Request Indexing feature in Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool to ask Google to crawl it sooner.
What happens if a page is not crawled or indexed?
If a page isn’t crawled or indexed, it is invisible in Google Search. The consequences are significant:
- No Search Visibility: The page will not appear in search results for any keywords, no matter how well-optimized it is.
- Lost Organic Traffic: Potential customers searching for your products or services will not find you, sending traffic to your competitors instead.
- Missed Business Opportunities: The investment made in creating the page generates no return, as it cannot attract customers or leads.
- Inability to Rank: Ranking is impossible without indexing. In the context of google crawling, indexing, and ranking, indexing is the non-negotiable prerequisite for appearing in search results.
Conclusion: Putting It All Together for SEO Success
We’ve explored the interconnected journey of google crawling, indexing, and ranking. These three stages work in a sequence: crawling enables indexing, and indexing enables ranking. A weakness in one stage undermines the entire process.
Mastering this is not a one-time task. SEO is a long-term strategy that requires consistent attention and adaptation as Google’s algorithms and user behaviors evolve. What works today may need refinement tomorrow.
For franchise businesses, these challenges are magnified. Ensuring every location is properly crawled, indexed, and optimized for its local market requires specialized skill and strategic vision.
This is the complex challenge Latitude Park was built to solve. We help franchises achieve visibility and growth by mastering these fundamental processes across their entire network.
Armed with the knowledge from this guide, you are better equipped to improve your site’s performance. Whether you’re optimizing one location or one hundred, these principles are the foundation of search success.
Ready to take your franchise’s online presence to the next level? We’re here to help you steer the complexities of multi-location SEO. Learn more about our SEO services for keyword ranking and let’s open up your franchise’s full potential together.